Pivotal Survey: Indigenous Cultural Safety, Humility and Anti-Racism Practice Standard
On September 30, 2022, eleven BC health profession regulatory colleges adopted an Indigenous cultural safety, humility and anti-racism practice standard. The standard sets clear expectations for how registrants are to provide culturally safe and anti-racist care for Indigenous clients and patients. In February 2023, ten of these colleges circulated a survey to their registrants.
With input obtained from both Indigenous and non-Indigenous respondents we were better able to interpret the self-reports and understand the areas upon which clear focus is required. We thank all survey participants and provide a summary of our learning, below.
Purpose
The colleges sought to establish a baseline of non-Indigenous registrants’ attitudes, perceptions, and perspectives related to Indigenous-specific racism in general and particularly in healthcare settings. The survey will be re-administered to measure change over time.
We also sought to gather information from Indigenous and non-Indigenous registrants about barriers to the implementation of the standard in their practices, and their learning needs related to the Core Concepts.
Respondents
We heard from 3,361 registrants from the ten colleges representing 12.2% of those who received a link to the survey. Three percent (3%) of respondents self-identified as Indigenous.
Survey Development
The survey questions were developed collaboratively by Pivotal Research (research consultants), Qoqoq (Indigenous consulting firm), and the ten participating colleges. Included were questions about:
- Attitudes and perceptions about Indigenous-specific racism
- Perspectives on Indigenous-specific racism in healthcare settings
- Current behaviours which reflect each principle of each Core Concept of the practice standard
- Implementation of the practice standard
- Guidance and/or education required to implement the standard
- Learning intention (when learning will begin)
- Preferred education delivery method
- Overall perceptions about the new standard
- Behaviours observed in practice settings (Indigenous respondents only)
- Stereotypes of Indigenous peoples (non-Indigenous respondents only)
Non-Indigenous respondents were asked to consider their own attitudes, perceptions, perspectives, and behaviours; Indigenous respondents were asked to consider the attitudes, perceptions, perspectives and behaviours of non-Indigenous colleagues in the same profession. Some questions were asked only of non-Indigenous respondents; others were asked only of Indigenous respondents. A trigger warning was included in the introduction of the survey, recognizing that some statements could be harmful.
TRIGGER WARNING: The results described below contain statements and descriptions of racism and negative experiences that may be triggering to some.
What We Learned
|
Interpretation of Survey Results The overall margin of error was +/- 1.76%, 19 times out of 20. Comparisons between Indigenous and non-Indigenous should be interpreted cautiously given the sensitivity of the topic and the relatively small number of Indigenous respondents. The individual responses to the survey were kept confidential by Pivotal Research and were not reported or shared with any of the colleges. All reporting was in aggregate. |
These results are a summary of the themes within the responses. While there were some differences in responses between colleges, these were not substantial enough to warrant reporting separately. In general, input was similar regardless of health profession.
- There is a continuum of attitudes and perceptions about Indigenous-specific racism reported by non-Indigenous respondents. Some agreed or strongly agreed with statements that represent stereotyping and contribute to perpetuating unsafe care and health inequities for Indigenous people. For example:
- 7% of non-Indigenous respondents strongly agreed/agreed with the statement “Colonialism is old news, we’ve all lived here for hundreds of years now, Indigenous Peoples should get over it.”
- 10% of non-Indigenous respondents strongly agreed/agreed with the statement “As a society, we’re being too accommodating to Indigenous Peoples.”
- 20% of non-Indigenous respondents strongly agreed/agreed with the statement “Indigenous people have problems with drugs and alcohol.”
- 13% of non-Indigenous respondents strongly agreed/agreed with the statement “Indigenous people get a lot of stuff for free that others have to work hard for.”
- The longer a non-Indigenous health professional has been in practice, the more likely they are to:
- say leaders in the workplace setting have set accountability outcomes to ensure the elimination of Indigenous-specific racism.
- agree with the stereotype that Indigenous people have issues with drugs and alcohol.
- indicate they learn about Indigenous communities located where they work.
And the less likely they are to:
- report acts of racism to leadership and/or the relevant health regulatory college.
- believe the new Standard should have been adopted much sooner.
- The attitudes, perceptions, perspectives and behaviours of non-Indigenous respondents as self-reported differ from the words and behaviours observed by their Indigenous colleagues. This was consistent to various degrees throughout the results. While many non-Indigenous respondents believe their intentions and actions reflect safe and respectful care, the impact of their actions, as noted by Indigenous colleagues, is often not what it is believed to be. For example:
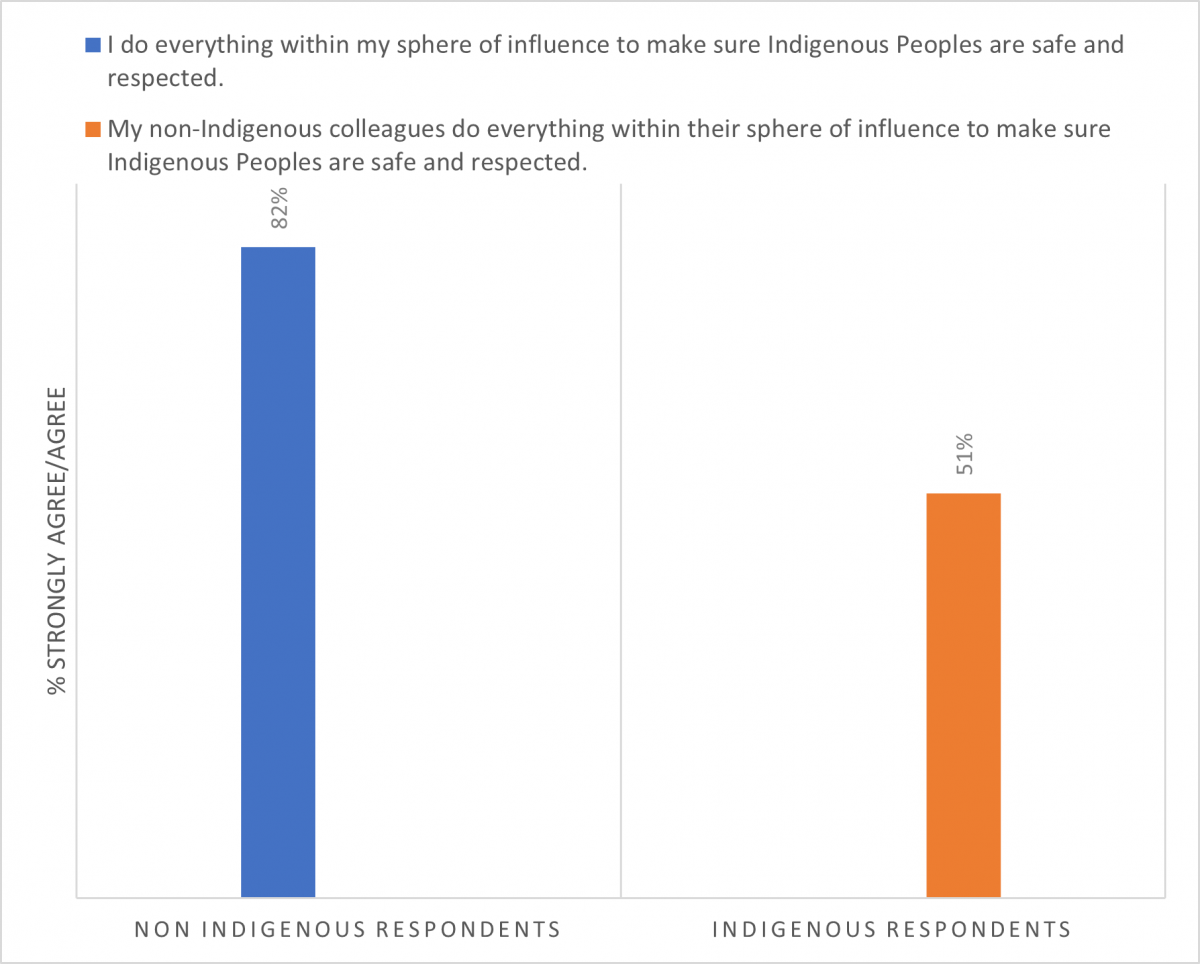
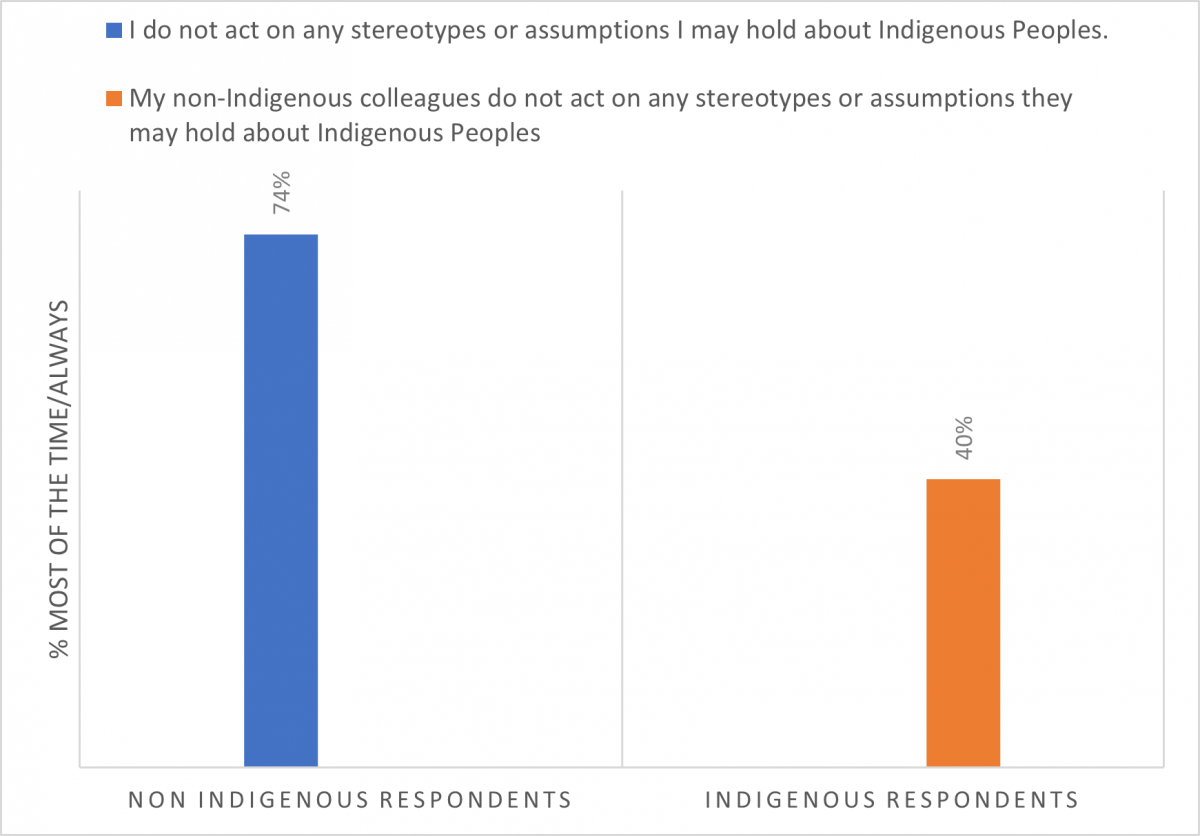
- 11%-12% of Indigenous respondents indicated that in the past year they have observed behaviours in their non-Indigenous colleagues such as failing to communicate adequately with Indigenous patients/clients and minimizing the concerns of Indigenous patients/clients.
- Indigenous-specific racism exists beyond public healthcare settings. Eighty percent (80%) of all respondents recognize that Indigenous-specific racism is a problem in public and private healthcare settings alike.
- Commonly reported barriers to implementation of the new standard were competing priorities, overwhelming workload and being unsure of what learning opportunities are available/appropriate. However, 33% of respondents reported they have no barriers to implementation.
- Between 13% and 31% (varied by Core Concept) of respondents require further guidance and education to implement the standard. The preferred delivery methods for educational offerings were webinars and short reads. Of those who indicated a need for further guidance and education, 50% intended to start or continue their learning within three months.
Summary
These results provide an important baseline measure of attitudes, perceptions, perspectives, and behaviours of health profession registrants against which progress and change will be measured in the future.
The value of the participation of self-identified Indigenous respondents can not be overstated. As we (health professionals and health profession regulators) work to ensure Indigenous clients and patients receive culturally safe care, only Indigenous clients and patients can confirm we have achieved that outcome. Indigenous health professional colleagues help the colleges understand and reflect upon our progress (or lack thereof) by offering their perspectives on how their colleagues and the system are performing.
Next Steps
These results also provide insight to health profession regulators about the barriers to implementation of the standard and the guidance and education that our registrants need to move to implementation. We will now work together to meet those needs.
LINK TO FULL REPORT
|
Existing Learning Resources
Registrants are encouraged to become familiar with the content, expectations, and intent of the practice standard in order to meet their regulatory commitments. The College of Pharmacists of BC has resources available for review about cultural safety, humility and Indigenous anti-racism posted on our website. Additionally, the BCCNM and the CPSBC have generously allowed all to access resources they created to support registrants at the time of publication of the standard. These can be found at the following links.
BCCNM Indigenous Cultural Safety, Cultural Humility and Anti-Racism Companion Guide
- BCCNM Introduction
- BCCNM Self Reflective Practice (It starts with me)
- BCCNM Building Knowledge Through Education
- BCCNM Anti-Racist Practice (Taking action)
- BCCNM Creating Safe Healthcare Experiences
- BCCNM Person-Led Care (Relational care)
- BCCNM Strengths-based and Trauma-informed Practice (Looking beneath the surface)